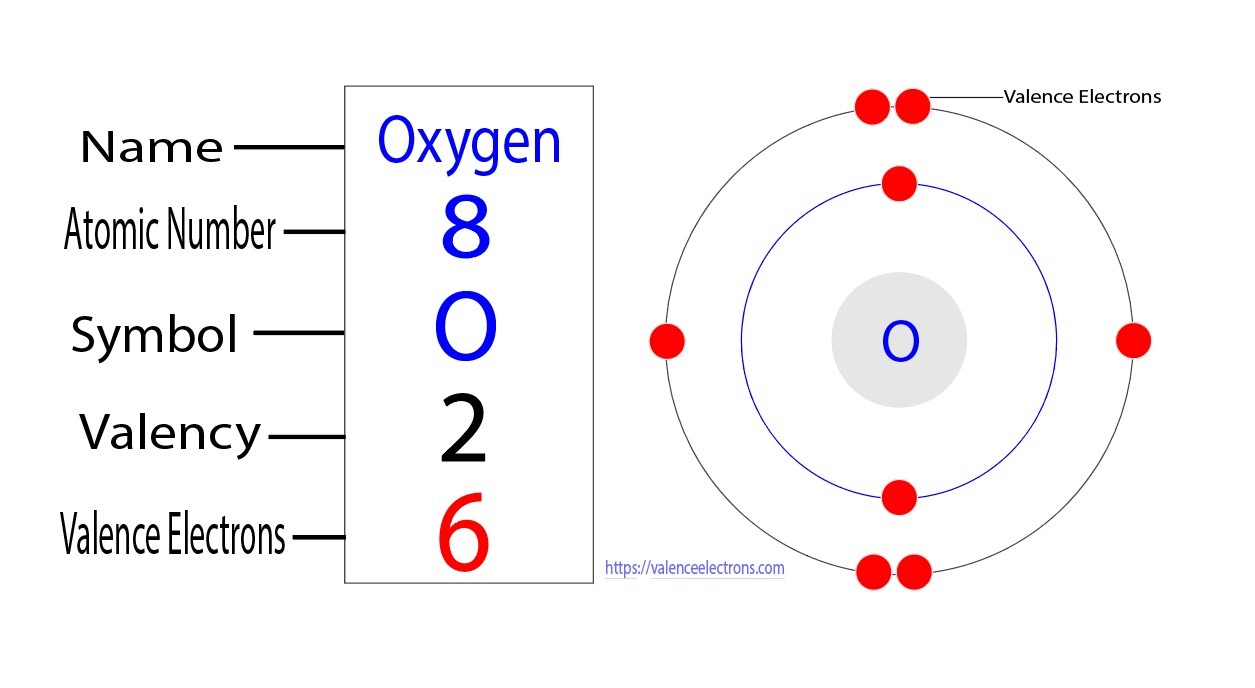
Oxygen has six valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons in an atom is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior.
In the case of oxygen, having six valence electrons gives it a stable configuration. This characteristic enables oxygen to readily form bonds with other elements, making it an essential component in various chemical reactions. Additionally, the presence of six valence electrons in oxygen contributes to its role in supporting life processes, such as respiration and combustion.
By grasping the significance of the valence electrons in oxygen, scientists can gain valuable insights into its reactivity and role in the natural world.
Credit: praxilabs.com
The Basics Of Valence Electrons
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons. Valence electrons are crucial for chemical bonding and determine an element’s reactivity. Understanding their role is fundamental in chemistry studies.
Defining Valence Electrons
Valence electrons play a crucial role in understanding the chemical properties of an element. But what exactly are valence electrons? In simple terms, valence electrons are the electrons found in the outermost energy level or shell of an atom. These electrons are involved in bonding with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. The number of valence electrons an atom has determines its reactivity and the types of bonds it can form.
Why Valence Electrons Matter
Valence electrons are essential for understanding an element’s behavior and its interactions with other elements. Here’s why they matter:
- Chemical Reactivity: The number of valence electrons determines an atom’s chemical reactivity. Atoms with fewer valence electrons tend to gain or share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration, while atoms with more valence electrons tend to lose or share electrons. This reactivity affects how elements combine to form compounds.
- Bonding: Valence electrons are directly involved in chemical bonding. Atoms with incomplete valence shells tend to form bonds with other atoms to achieve a more stable configuration. This bonding can result in the formation of ionic, covalent, or metallic bonds, depending on the electronegativity and properties of the atoms involved.
- Chemical Properties: The number and arrangement of valence electrons determine an element’s chemical properties. Elements within the same group in the periodic table often have similar chemical properties because they have the same number of valence electrons. For example, oxygen, with six valence electrons, exhibits properties like its ability to form stable oxides and participate in combustion reactions.
- Periodic Trends: Valence electrons contribute to periodic trends such as atomic radius, ionization energy, and electronegativity. Elements with more valence electrons generally have larger atomic radii and lower ionization energies, making them more likely to lose electrons and form positive ions. Electronegativity, which describes an atom’s tendency to attract electrons, increases as the number of valence electrons decreases.
By understanding the basics of valence electrons and their significance, we can gain valuable insights into the behavior of elements and their involvement in chemical reactions. This knowledge forms the foundation for understanding the complexities of chemical bonding and the properties of various compounds.
Credit: socratic.org
Oxygen’s Place In The Periodic Table
Oxygen’s Group And Period
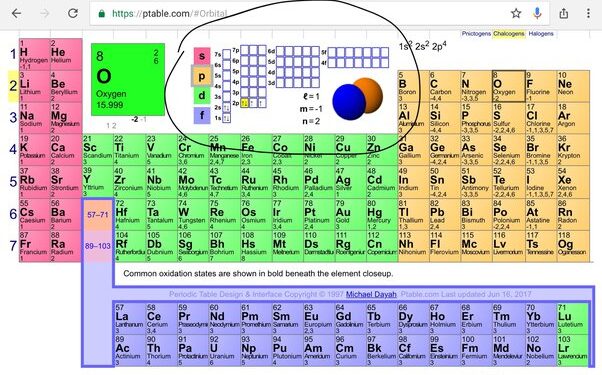
Oxygen, with the atomic number 8, belongs to Group 16 and Period 2 of the periodic table.
Comparing Oxygen With Neighboring Elements
Oxygen can be compared with its neighboring elements, such as carbon and nitrogen, to understand its chemical properties.
Determining Oxygen’s Valence Electrons
Oxygen has six valence electrons, which determine its chemical behavior and reactivity. Understanding the number of valence electrons in oxygen is crucial for predicting its bonding patterns and forming chemical compounds. By recognizing the role of these electrons, scientists can gain valuable insights into oxygen’s interactions with other elements.
The Electron Configuration Of Oxygen
Oxygen is a chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. To determine the valence electrons of oxygen, we first need to understand its electron configuration. The electron configuration of an atom describes the arrangement of electrons in its various energy levels or shells. In the case of oxygen, its electron configuration can be represented as 1s² 2s² 2p⁴. This means that oxygen has two electrons in its first energy level (1s), two electrons in its second energy level (2s), and four electrons in its third energy level (2p).Calculating Valence Electrons
Valence electrons are the electrons present in the outermost energy level of an atom. These electrons are responsible for the chemical properties and reactivity of the element. To calculate the valence electrons of oxygen, we need to focus on the electrons in its outermost energy level. In the case of oxygen, the outermost energy level is the second energy level (2s² 2p⁴). Since there are two electrons in the 2s sublevel and four electrons in the 2p sublevel, the total number of valence electrons in oxygen is six. Therefore, oxygen has six valence electrons, which makes it highly reactive and capable of forming various compounds with other elements. To summarize: – Oxygen’s electron configuration is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴. – The outermost energy level of oxygen is the second energy level (2s² 2p⁴). – Oxygen has a total of six valence electrons. Understanding the number of valence electrons in an element like oxygen is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and interactions with other elements. By knowing the valence electrons, scientists can determine the element’s ability to form bonds and participate in chemical reactions.
Credit: www.youtube.com
The Role Of Oxygen’s Valence Electrons In Bonding
The Role of Oxygen’s Valence Electrons in Bonding
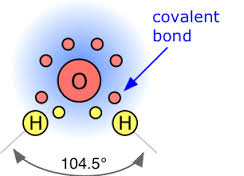
Covalent Bonding Explained
In covalent bonding, atoms share pairs of valence electrons to achieve a stable configuration.
Examples Of Oxygen Bonds
Oxygen forms covalent bonds with hydrogen to create water molecules.
Valence Electrons And Chemical Reactivity
Valence electrons play a crucial role in determining an element’s chemical reactivity. Understanding the valence electrons of oxygen is essential for comprehending its behavior in chemical reactions.
Oxygen’s Reactivity
Oxygen, with 6 valence electrons, is highly reactive. It readily forms compounds with many other elements due to its strong tendency to gain or share electrons.
Influence Of Valence Electrons On Reactivity
The number of valence electrons directly influences an element’s reactivity. Elements with a full outer shell, like noble gases, are inert, while those with few valence electrons tend to be highly reactive.
Visualizing Oxygen’s Valence Electrons
Oxygen has six valence electrons, which are crucial for understanding its reactivity and bonding behavior. Visualizing oxygen’s valence electrons can help in comprehending its role in various chemical reactions and compound formations. Understanding the number of valence electrons oxygen has is fundamental in predicting its chemical properties.
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons, which are crucial for its chemical reactivity.Orbital Diagrams
The orbital diagram for oxygen shows two electrons in the 1s orbital, two electrons in the 2s orbital, and two electrons in the 2p orbital.Lewis Dot Structures
In a Lewis Dot Structure, oxygen is represented by the symbol O with 6 dots surrounding it, indicating its 6 valence electrons.Oxygen In Everyday Chemistry
Oxygen, an essential element in everyday chemistry, possesses six valence electrons. These electrons play a crucial role in forming chemical bonds and determining the reactivity of oxygen in various chemical reactions. Understanding the valence electrons of oxygen is fundamental in comprehending its behavior and involvement in numerous chemical processes.
Oxygen In Water
Oxygen in water is essential for aquatic life.
Oxygen’s Role In Combustion
Oxygen fuels fires and supports combustion reactions.
Advanced Topics: Oxygen’s Valence Electrons
Oxygen has six valence electrons. Understanding the valence electrons of oxygen is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and its ability to form bonds with other elements. The six valence electrons in the outer shell of an oxygen atom make it a key player in various chemical reactions.
Valence In Molecular Orbitals
Oxygen’s valence electrons play a crucial role in forming molecular orbitals.
These orbitals determine the chemical reactivity and bonding properties of oxygen compounds.
Valence Electrons In Oxides
Oxygen typically exhibits a valence of -2 in oxides.
This is due to the tendency of oxygen to gain electrons to achieve a stable octet configuration.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Valence Electrons Does Oxygen Have?
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
Why Are Valence Electrons Important?
Valence electrons determine the reactivity and chemical properties of an element.
How Do You Determine The Number Of Valence Electrons?
The number of valence electrons can be determined by the element’s group number on the periodic table.
What Is The Octet Rule?
The octet rule states that atoms tend to gain, lose, or share electrons in order to have a full outer shell of 8 electrons.
Conclusion
Oxygen has six valence electrons, making it a highly reactive element. These electrons are responsible for forming covalent bonds with other elements, such as hydrogen, to create water molecules. Understanding the number of valence electrons an element has is crucial in predicting its chemical behavior and reactivity.
By knowing the valence electron count of oxygen, scientists can better understand and manipulate its properties for various applications. Overall, oxygen’s six valence electrons play a significant role in its chemical behavior and interaction with other elements.