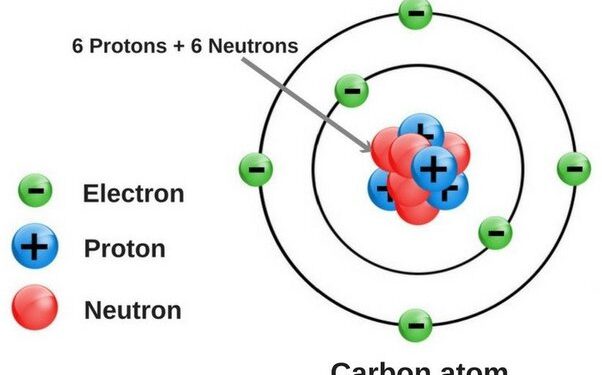
Oxygen has 8 electrons. It is located in the 2nd energy level.
Oxygen is a crucial element in the periodic table with 8 electrons. It plays a vital role in various natural and industrial processes. Understanding its electron configuration is essential for comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. In this blog, we will delve into the significance of oxygen, its electron count, and its impact on the world around us.
By the end, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the role of oxygen electrons and their importance in different chemical reactions and biological processes.
Credit: socratic.org
The Basics Of Oxygen
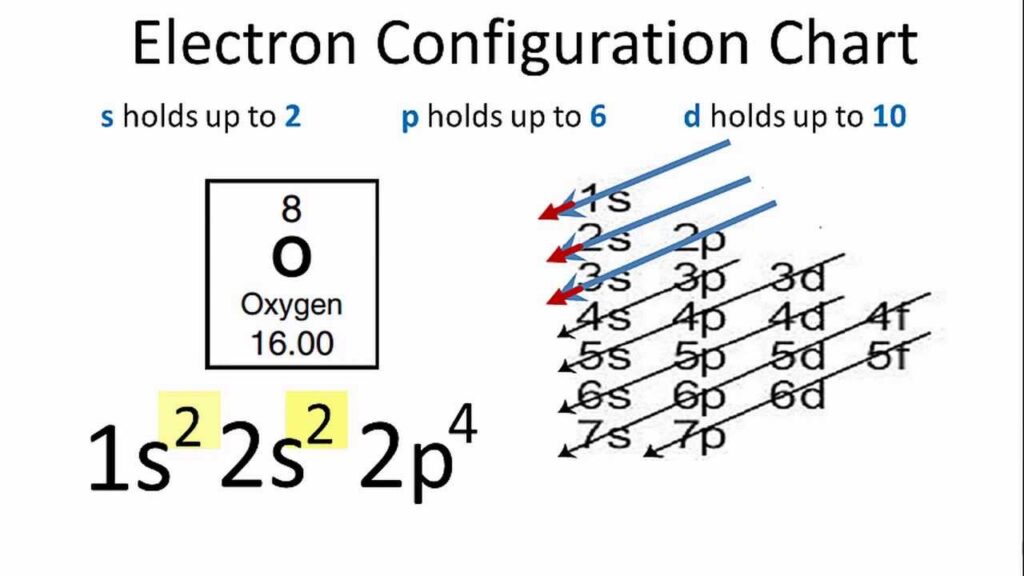
Oxygen has 8 electrons in its outer shell, making it highly reactive in chemical reactions. Its electron configuration is 1s2 2s2 2p4.
Atomic Structure
Oxygen is an element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It has 8 protons and 8 electrons in its atomic structure. The number of neutrons in oxygen’s nucleus can vary, leading to different isotopes of the element. The most common isotope of oxygen is ^16O, which has 8 neutrons.
Oxygen’s Place In The Periodic Table
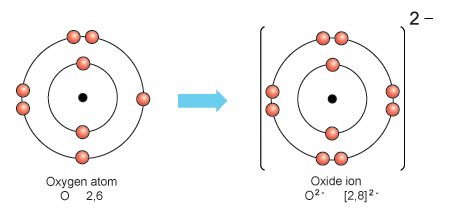
Oxygen is a member of the chalcogen group on the periodic table, along with sulfur, selenium, and tellurium. It is located in group 16, also known as the oxygen group, and period 2. Oxygen is a highly reactive nonmetal and is essential for life as we know it. It is the third most abundant element in the universe, after hydrogen and helium, and the most abundant element by mass in the Earth’s crust.
Properties Of Oxygen
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless gas at room temperature and pressure. It is a highly reactive element and readily forms compounds with other elements, such as water, carbon dioxide, and many organic compounds. Oxygen is essential for combustion, and it supports life by being a major component of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is also used in many industrial processes, such as steelmaking and welding.
Credit: www.quora.com
Electrons And Their Orbitals
Oxygen has 8 electrons, with 6 of them occupying the outer orbital. This makes oxygen a reactive element, as it needs 2 more electrons to complete its outer shell.
What Are Electrons?
Electrons are tiny, negatively charged particles that orbit around the nucleus of an atom. They are one of the fundamental building blocks of matter and play a crucial role in the behavior and properties of atoms and molecules.
Understanding Orbitals
Orbitals are regions within an atom where electrons are most likely to be found. Each orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, and they are categorized into different types based on their shape and energy levels.
There are four types of orbitals: s, p, d, and f. The s orbital is spherical in shape and is the closest to the nucleus. The p orbitals are dumbbell-shaped and exist in sets of three, designated as px, py, and pz. The d orbitals have more complex shapes and exist in sets of five, while the f orbitals have even more intricate shapes and exist in sets of seven.
The number of orbitals in each type increases with the principal quantum number (n), which represents the energy level of the electrons. For example, in the first energy level (n=1), there is only one s orbital. In the second energy level (n=2), there are one s and three p orbitals. In the third energy level (n=3), there are one s, three p, and five d orbitals. And so on.
It’s important to note that electrons fill up orbitals in a specific order, following the Aufbau principle. This principle states that electrons occupy the lowest energy orbitals first before moving to higher energy levels.
Here’s a breakdown of the maximum number of electrons each type of orbital can hold:
| Type of Orbital | Maximum Number of Electrons |
|---|---|
| s | 2 |
| p | 6 |
| d | 10 |
| f | 14 |
Understanding the arrangement of electrons in orbitals is crucial in predicting chemical reactivity and the formation of chemical bonds. It provides insights into the behavior and properties of elements and compounds, allowing scientists to unravel the mysteries of the atomic world.
Counting Oxygen’s Electrons
Valence Electrons
Oxygen has 6 valence electrons.
Total Electron Count
Oxygen has a total of 8 electrons.
The Significance Of Electron Configuration
Oxygen, as an element, has 8 electrons. Understanding its electron configuration is significant in comprehending its chemical behavior and reactivity. By knowing the arrangement of electrons in an atom, we can gain insights into the element’s properties and its interactions with other elements.
Energy Levels
The concept of electron configuration is essential in understanding the behavior of atoms and their chemical properties. Electrons are arranged in specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus of an atom. These energy levels, labeled as n=1, n=2, n=3, and so on, correspond to increasing distances from the nucleus.
Each energy level can hold a maximum number of electrons. The first energy level (n=1) can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, while the second energy level (n=2) can hold a maximum of 8 electrons. The subsequent energy levels can accommodate even more electrons.
Electron Configuration In Oxygen
Oxygen is an element with atomic number 8, meaning it has 8 electrons. To determine its electron configuration, we follow the Aufbau principle, which states that electrons fill the lowest energy levels first before moving to higher energy levels.
Oxygen’s electron configuration can be represented as 1s2 2s2 2p4. Let’s break it down:
- The first energy level (n=1) has a single s orbital, which can hold a maximum of 2 electrons. Oxygen fills this orbital with 2 electrons, represented as 1s2.
- The second energy level (n=2) has both s and p orbitals. The 2s orbital can hold a maximum of 2 electrons, and the 2p orbital can hold a maximum of 6 electrons. Oxygen fills the 2s orbital with 2 electrons, represented as 2s2. It then fills the 2p orbitals with 4 electrons, represented as 2p4.
By understanding the electron configuration of oxygen, we gain insights into its reactivity and chemical bonding behavior. The arrangement of electrons in the outermost energy level (valence electrons) influences an atom’s ability to form bonds with other atoms and participate in chemical reactions.
Oxygen In Chemical Bonds
Covalent Bonding
Oxygen typically forms covalent bonds with other elements, sharing its six electrons to complete its outer shell. This type of bonding occurs when two atoms share a pair of electrons, resulting in a stable configuration for both atoms. In the case of oxygen, it can form covalent bonds with other oxygen atoms to create O2 molecules, or with elements like hydrogen to form water (H2O).
Ionic Bonding
Oxygen can also participate in ionic bonding by gaining or losing electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. In ionic bonds, one atom donates one or more electrons to another atom, resulting in the formation of positively and negatively charged ions that are attracted to each other. For example, in compounds like sodium oxide (Na2O), oxygen gains electrons to become a negatively charged ion, while sodium loses electrons to become a positively charged ion, leading to the formation of an ionic bond.
Oxygen’s Role In Life And The Environment
Oxygen, with eight electrons, plays a crucial role in supporting life and maintaining environmental balance. Its electron configuration allows it to form bonds with other elements, facilitating essential processes such as respiration and photosynthesis in living organisms. In the environment, oxygen’s electron structure enables it to participate in chemical reactions that drive the Earth’s cycles and sustain ecosystems.
Breathing And Respiration
Oxygen is vital for breathing and respiration.
Humans and animals depend on oxygen to survive.
It enables cells to produce energy efficiently.
Ozone And Atmospheric Protection
Oxygen plays a key role in forming ozone.
Ozone layer shields Earth from harmful UV rays.
Protects life on Earth from excessive radiation.
Experimental Determination Of Electron Count
The experimental determination of electron count reveals that oxygen has 8 electrons in its atomic structure. This information is crucial in understanding oxygen’s chemical behavior and its role in various reactions.
Spectroscopy Techniques
Quantum Mechanics Insights
Experimental determination of electron count in oxygen is crucial for understanding its reactivity. Spectroscopy Techniques allow scientists to study oxygen’s electron configuration. – X-ray spectroscopy reveals inner-shell electrons. – UV-Vis spectroscopy detects outer-shell electrons. Quantum Mechanics Insights help explain oxygen’s electron behavior. – Pauli Exclusion Principle limits electrons per orbital. – Quantum numbers describe electron energy levels. In conclusion, combining experimental techniques and quantum principles helps uncover oxygen’s electron count.
Credit: www.chem4kids.com
Applications And Implications
Oxygen has 8 electrons in its atomic structure, with 6 of them in the valence shell. This allows for oxygen to form covalent bonds with other elements, making it an essential component in organic molecules and the process of respiration.
Technological Applications
Oxygen’s presence is crucial in various technological applications.
- Used in steelmaking for oxidation reactions.
- Supports combustion in engines and industrial processes.
- Essential in medical therapies and life support systems.
Environmental Impact
Oxygen levels in the environment impact various aspects.
- Supports aquatic life through oxygenation of water bodies.
- Regulates atmospheric composition for sustaining life.
- Contributes to oxidation of pollutants in the air and water.
Frequently Asked Questions
How Many Electrons Does An Oxygen Atom Have?
An oxygen atom has 8 electrons, with 2 in the inner shell and 6 in the outer shell. Electrons play a crucial role in the chemical behavior of oxygen.
Why Is The Number Of Electrons In Oxygen Important?
The number of electrons in oxygen determines its chemical properties, such as its ability to form bonds with other atoms to create compounds.
What Is The Significance Of Oxygen’s Electron Configuration?
Oxygen’s electron configuration influences its reactivity and bonding behavior, making it essential for various biological and chemical processes in nature.
Conclusion
Oxygen is a vital element for life on Earth, and understanding its atomic structure is crucial. By delving into the number of electrons oxygen has, we can gain a deeper understanding of its chemical properties and behavior. With eight electrons in its outermost shell, oxygen is highly reactive and readily forms compounds with other elements.
This knowledge is essential in various fields, including biology, chemistry, and physics, making it a fundamental concept to grasp.
Mastering the creation of internet in Infinity Craft can enhance your gameplay and experience. Follow the steps outlined above to achieve this empowering feat. For a comprehensive guide, check out our article: How to Make Internet in Infinity Craft: Ultimate Empowering Guide.